Learn Manual Testing From Scratch Part 1
SDLC: -
Software Development Life Cycle
It is a procedure to
develop the software.
It is a process of creating
or altering systems and the models and methodologies that people use to develop
these systems.
Any SDLC should result in a
high quality system that meets or exceeds customer expectations, reaches
completion within time and cost estimates, works effectively and efficiently
and is inexpensive to maintain and cost effective to enhance.
Different procedures /
models are available to develop a software namely,
1) Waterfall model
It is a traditional model
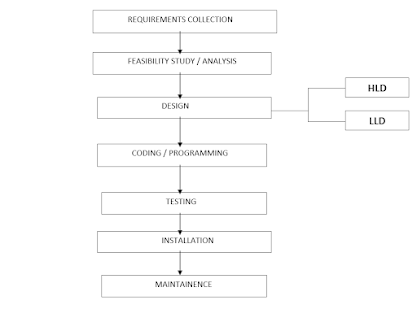
It is a sequential design process, often used in SDLC, in which the progress is seen as flowing steadily downwards (like a waterfall), through the different phases as shown in the figure,
Requirements
Collection :-
- done by Business Analysts
and Product Analysts
- gathering requirements
- translates business
language into software language
For
ex, let us
consider the example of a banking software.
Feasibility
Study :-
- done by software team
consisting of project managers, business analysts, architects, finance, HR,
developers but not testers
- architect – is the person
who tells whether the product can be developed and if yes, then which
technology is best suited to develop it.
- here we check for,
- technical feasibility
- financial feasibility
- resource feasibility
Design
:-
There are 2 stages in
design,
HLD – High Level
Design
LLD – Low Level
Design
HLD – gives the
architecture of the software product to be developed and is done by architects
and senior developers
LLD – done by senior
developers. It describes how each and every feature in the product should work
and how every component should work. Here, only the design will be there and
not the code.
For
ex, let us
consider the example of building a house.
Coding
/ Programming :-
- done by all developers –
seniors, juniors, freshers
- this is the process where
we start building the software and start writing the code for the product.
Testing
:-
- done by test engineers
- it is the process of
checking for all defects and rectifying it.
Installation
:-
- done by installation
engineers
- to install the product at
a client’s place for using after the software has been developed and tested.
For
ex, consider
the example of a software to be developed and installed at Reliance petrol
bunk.
Maintenance:-
- here as the customer uses
the product, he finds certain bugs and defects and sends the product back for
error correction and bug fixing.
- bug fixing takes place
-
minor changes like adding, deleting or modifying any small feature in the
software product
100 % testing is not
possible – because, the way testers test the product is different from the way
customers use the product.
Service – based companies and Product – based
companies
Service
– based companies: -
They provide service and
develop software for other companies
They provide software which
is and specified as per the client company’s requirement and never keep the
code of the developed product and does not provide the software to any other
company other than the client company.
Ex – Wipro, Infosys, TCS,
Accenture
Product
– based companies :-
The develop software
products and sell it to many companies which may need the software and make
profits for themselves
They are the sole owners of
the product they develop and the code used and sell it to other companies which
may need the software.
Ex – Oracle, Microsoft
Drawbacks of Waterfall Model :-
In waterfall model,
backtracking is not possible i.e, we cannot back and change requirements once
the design stage is reached. Change in requirements – leads to change in design
– thus bugs enter the design – which leads to change in code which results in
more bugs. Thus the requirements are freezed once the design of the product is
started.
Drawback of requirements freezing – the customer may not be satisfied if the changes he requires is not incorporated in the product. The end result of waterfall model is not a flexible product.
Major drawback of waterfall
model – testing is a small phase which is done after coding. Requirement is not
tested, design is not tested, if there is a bug in the requirement, it goes on
till the end and leads to lot of re-work.
Advantages of waterfall model – requirements do not
change nor does design and code, so we get a stable product.
Applications of waterfall model :-
Used in – developing a
simple application
- for short term projects
- whenever we are sure that the
requirements will not change
For ex, waterfall model can be used in developing a simple calculator as the functions of addition, subtraction etc and the numbers will not change for a long time.
2 ) SPIRAL MODEL
The spiral model is shown
in the figure in the next page.
Ra- requirements analysis
of module A. Similarly with Rb, Rc, Rd.
Da – design of module A.
Similarly with Db, Dc, Dd
Ca – coding of module A.
Similarly with Cb, Cc, Cd
Ta – testing of module A.
Similarly with Tb, Tc, Td
In Spiral model, the
software product is developed in small modules. Let us consider the figure
shown below in developing a s/w product X. X is built by integrating A,B,C and
D.
The module A – requirements
of the module is collected first and then the module is designed. The coding of
module A is done after which it is tested for defects and bugs.
The module B – once module
A has been built, we start the same process for module B. But while testing
module B, we test for 3 conditions – a)test module B b)test integration of
module B with A c)test module A.
The module C – after
building module A,B, we start the same process for module C. Here we test for
the following conditions – 1) test module c, b, a 2) test for integration of C
and B, C and A, A and B.
And thus the cycle
continues for different modules. Thus in the above example, module B can be
built only after module A has been built correctly and similarly for module C.
Here we have to create the
cells first (module A). Then we can do operations on the cells like merge cells
into two , split cell into half (module B ). Then we can draw graphs on the
excel sheet (module C).
Advantages of Spiral Model
:-
1) Requirement changes are allowed.
2) After we develop one feature / module of the
product, then only we can go on to develop the next module of the product.
Whenever the customer
request for major changes in requirements in a particular module, then
we change only that module and do testing of both unit and integration of
units. This change in requirements comes up in a separate cycle just to do the
changes.
Whenever the customer
request minor changes in the product, then the s/w team makes the minor
changes along with the new module to be developed simultaneously in a single
cycle. We don’t consider making the minor change in a separate cycle of the
spiral model due to time and resource constraints.
The documents collected by
Business analysts during requirement collection stage is known as CRS ( Customer Requirement Specification ) or
BRS ( Business Requirement Specification
) or BS ( Business Specification ).
In this document , the client explains how their business works or the
requirement of the s/w he needs. The BA gathers CRS from the client and
translates it into SRS ( Software
Requirement Specification ). The SRS contains how the software should be
developed and is given by the BA to developers. For more detailed explanation
of how to go about developing the s/w, the BA/developer builds another document
– FS ( Functional Specification ). FS
explains how each and every component should work.
Drawbacks
of Spiral Model – Traditional
model and thus developers only did testing job as well.
Applications of Spiral Model
- whenever there is
dependency in building the different modules of the software, then we use
Spiral Model.
-
whenever the customer gives the requirements in stages, we develop the product
in stages.
3) V
– MODEL / V & V MODEL (Verification and Validation Model )
This model came up in order
to overcome the drawback of waterfall model – here testing starts from the
requirement stage itself.
The V & V model is
shown in the figure in the next page.
1) In the first stage, the client send the CRS both to developers and testers. The developers translate the CRS to the SRS.
The testers do the
following tests on CRS,
1. Review CRS
a. conflicts in the requirements
b. missing requirements
c. wrong requirements
2. Write Acceptance Test plan
3. Write Acceptance Test cases
The testing team reviews
the CRS and identifies mistakes and defects and send it to the development team
for correcting the bugs. The development updates the CRS and continues
developing SRS simultaneously.
2
) In the next stage, the
SRS is sent to the testing team for review and the developers start building
the HLD of the product. The testers do the following tests on SRS,
1. Review SRS
against CRS
a. every CRS is converted to SRS
b. CRS not converted properly to SRS
2. Write System Test plan
3. Write System Test case
The testing team reviews
every detail of the SRS if the CRS has been converted properly to SRS.
3
) In the next stage, the
developers start building the LLD of the product. The testers do the following
tests on HLD,
1. Review HLD
2. Write Integration test plan
3. Write Integration test case
4
) In the next stage, the
developers start with the coding of the product. The testing team carries out
the following tasks,
1. Review LLD
2. Write Functional test plan
3. Write Functional Test case
After coding, the developers themselves carry out unit testing or also known as white box testing. Here the developers check each and every line of code and if the code is correct. After white-box testing, the s/w product is sent to the testing team which tests the s/w product and carries out functional testing, integration testing, system testing and acceptance testing and finally deliver the product to the client.
How to handle
requirement changes in V&V:-
Whenever there is change in
requirement, the same procedure continues and the documents will be updated.
Advantages
of V&V model
1)
Testing
starts in very early stages of product development which avoids downward flow
of defects which in turn reduces lot of rework
2) Testing is involved in
every stage of product development
3) Deliverables are
parallel/simultaneous – as developers are building SRS, testers are testing CRS
and also writing ATP and ATC and so on. Thus as the developers give the
finished product to testing team, the testing team is ready with all the test
plans and test cases and thus the project is completed fast.
4)
Total
investment is less – as there is no downward flow of defects. Thus there is
less or no re-work
Drawbacks of V&V model
1)
Initial
investment is more – because right from the beginning testing team is needed
2)
More
documentation work – because of the test plans and test cases and all other
documents
Applications of V&V model
We go for V&V model in
the following cases,
1) for long term projects
2)
for
complex applications
3) when customer is expecting a very high quality product within stipulated time frame because every stage is tested and developers & testing team are working in parallel
4) PROTOTYPE DEVELOPMENT
MODEL
The requirements are
collected from the client in a textual format. The prototype of the s/w product
is developed. The prototype is just an image / picture of the required s/w
product. The customer can look at the prototype and if he is not satisfied,
then he can request more changes in the requirements.
Prototype testing means developers/ testers are checking if all the components mentioned in requirements are existing or not.
The difference b/w
prototype testing and actual testing – in PTT, we are checking if all the
components are existing, whereas, in ATT we check if all components are working.
From “REQUIREMENT COLLECTION” to
“CUSTOMER REVIEW”, textual format has been converted to image format. It is
simply extended requirement collection stage. Actual design starts from “DESIGN”
stage.
Prototype development was earlier done
by developers. But, now it is done by web designers/content developers. They
develop prototype of the product using simple ready-made tools. Prototype is
simply an image of the actual product to be developed.
Advantages
of Prototype model
1) In the beginning itself, we
set the expectation of the client.
2) There is clear
communication b/w development team and client as to the requirements and the
final outcome of the project
3) Major advantage is –
customer gets the opportunity in the beginning itself to ask for changes in
requirements as it is easy to do requirement changes in prototype rather than
real applications. Thus costs are less and expectations are met.
Drawbacks
of Prototype model
1) There is delay in starting
the real project
2) To improve the
communication, there is an investment needed in building the prototype.
Applications
We use this model when,
1) Customer is new to the s/w
2) When developers are new to
the domain
3)
When
customer is not clear about his own requirement
There are 2 types of prototype,
Static
Prototype – entire
prototype of the requirement is stored in a word document with explanation and
snapshots and instructions on how to go about building the s/w, how the
finished product will look like and its working etc.
Dynamic
Prototype – similar
to a browser, but we can’t enter any information. Only the features are
available without entering data. It’s like a dummy page, made out of HTML with
tags and links to different pages representing features of the project
5)
Derived model or Customized model – we can take any of the
above 4 models and change it as per business needs and requirements
6) HYBRID MODEL
It combines 2 or more models and
modify them as per business requirements.
A) Hybrid
model of Spiral and Prototype development models
We go for
this model when,
1) Whenever there is
dependency, we go for this hybrid model
2) When the customer gives
requirement in stages, we develop the product in stages using this hybrid model.
3) When the customer is new
to the s/w domain
4) When developers are new to
the domain
5) When customer is not clear
about his own requirements
Hybrid
model of V&V and Prototype model
We go for
this model when,
1) Testing starts from early
stages of product development which avoids downward flow of defects, thus
reducing re-work.
2) When customer is expecting
a very high quality product within stipulated time frame because every stage is
tested and developers and testing team work in parallel.
3) When client and developers
are both new to the domain
4) When customer is not clear
about his own requirements
In this hybrid model, the testing team is involved in testing the prototype.
Note : There is one more model introduced and that is Agile . It is a very powerful model all IT organizations using . Please go through online to know more about this model
INTERVIEW QUESTIONS
1) What is SDLC ?
2) What are the different models available ?
ANS) Tell the 1st 6 models and 7)RUP – Rational Unified Process Model 8) Agile Model
9) RAD – Rapid Application Development
3) Advantages, Disadvantages and Applications of each model
4) A model for every project in our resume -> for 3 projects we
do, be prepared to tell which model we used for each project and why we used
that particular model only. The most common answer we can tell – we used a hybrid
of “so and so” model for the reasons such as – client was not sure of his
requirements, etc .





Comments
Post a Comment